Greece Travel Guide
Greece is suitable for sea holiday with its islands and beaches, as well as being the home of many civilizations in the past and may be preferred for cultural tourism. 18 different sites in the country are included in the UNESCO World Heritage List. People from all over the world travel to Greece for their islands and historic cities, famous for their sun and coast. In addition to its sunny weather and magnificent beaches, a holiday in Greece is quite affordable.
Visiting Greece, with its delicious Greek food, windy but relaxing islands, and lively and hospitable locals, is an ideal choice for European travel. Before you go to Greece, you can arrange your itinerary according to the travel guide we have prepared for you.
General Information
| Language | Greek |
| Capital City | Athens |
| Continent | Southeast Europe |
| Population | 11 million |
| Local Time | GMT+3 |
| Currency | Euro |
| Plug Type | C, F |
| Mean Yearly Temperature | 18°C |
| Climate | Mediterranean |
| Area | 131.957 km² |
| Government | Parliamentary Democracy |
| Vegetation | Scrub |
| Livelihood | Agriculture, Fishery, Tourism |
| Phone Code | +30 |
Official Language
Greek is the official language of Greece.
Capital City
With a history of 3,500 years, Athens is the capital of Greece and the largest city in the country.
Local Time
Greece uses GMT + 3 time zone.
Currency
The currency of Greece, which is a member of the European Union, is Euro.
Vegetation
Greece is generally divided into five regions: Macedonia, Thrace, Epirus, Thessaly, and Peloponnese. Almost four-fifths of the territory of Greece is mountainous and only a small part is plains. The low parts of Greece are poor in vegetation and single seasonal plants grow. In the central and southern parts of the country, the flora is characteristic of the Mediterranean climate. Forests are located in mountainous regions. Forests or groves occupy about 50% of the country.
Livelihood
The Greek economy is largely based on agriculture. Nearly 29% of its land is suitable for agriculture. Since most regions are mountainous, large and fertile plains suitable for agriculture and the number of streams required for irrigation are small. However, nearly 30% of the population is engaged in agriculture. Livestock is not developed as much as could have. For this reason, meat is purchased from foreign markets. Greece is a highly developed country in terms of fisheries. Greece is a very rich country in terms of underground mines. Although Greece is rich in mining, its contribution to the economy is very low. Nearly 30% of the country works in the manufacturing industry. Tourism is another major economic source for Greece.
Where is Greece?
Greece is a small country at the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula. It is a peninsula surrounded on three sides by the sea. Greece is surrounded by the Aegean Sea in the east and southeast, the Mediterranean Sea in the south and the Ionian Sea in the west. The coast of Greece is very indented and is approximately 150-160 km long. Almost 2,000 islands along the Aegean and Mediterranean coasts belong to Greece.
Best Time to Visit
Under the influence of the Mediterranean climate, Greece is warm in summer and warm and cool in winters. Greece has an average annual temperature of 18 °C. In winter, the lowest temperature is 7 ° C, and in summer the highest temperature is 34 °C. The ideal time to visit Greece is between May and October. This is the time to swim or dive, visit historical sites, take advantage of shopping opportunities or participate in activities that you can do all together. If you go to Greece in the summer, you can explore deep scuba diving and underwater caves, enjoy the archaeological sites and the scenery, have fun at the waterfront taverns, have fun at the beach bars until sunrise and have a great time by participating in traditional fairs and festivals.
How to Get to Greece?
There are air, sea and land transportation to Greece. The most ideal means of transportation is the airline. With Pegasus Airlines, you can fly from Istanbul to Athens Eleftherios Venizelos International Airport in approximately 1.5 hours every day.
Public Transportation in Greece
Buses are used for standard road transport in Greece. Train networks are limited. Buses cover most primary routes on the mainland and provide basic connections on the islands. As an alternative to buses, you can rent scooters, motorcycles or cars on the islands. The journey between the islands is via ferries and catamarans.
At the end of these trips, you can reach any of the Greek islands. Domestic flights are relatively expensive. Athens has developed in terms of public transport compared to other cities. In Athens, as well as buses and taxis, there are subways, trams and commuter lines. For a more comfortable journey, you can take advantage of Pegasus car rental service. You can book by entering your flight details before your trip.
Transportation from Athens Eleftherios Venizelos International Airport to City Center
Athens Eleftherios Venizelos International Airport is located 30 km east of Athens. There are many options to reach the city center from the airport. You can go to the city center by subway, train, bus or taxi, or you can use a shuttle or car rental services.
Places to Visit in Greece
As one of the most important centers of summer tourism, Greece has many cities and historical sites to visit. The 18 historical and natural sites on the UNESCO World Heritage List are located in Greece. Most of this rich heritage is from ancient Greece. The Acropolis in Athens is one of the most visited places in the country. Mount Olympos, the source of mythology, hosts thousands of tourists every year. Mystras Ruins, Mali Archaeological Site, Archaeological Museum of Heraklion are among the places you can visit. For those who want to swim and have fun in the sea, the islands such as Mykonos, Kos are the right place.
Athens
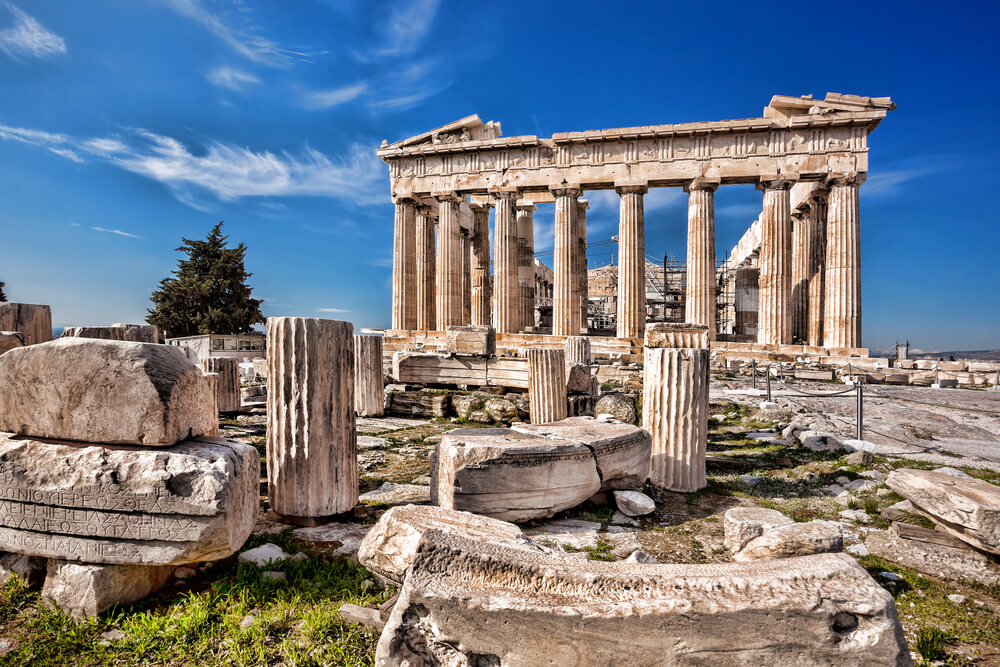

Athens, the capital of Greece and also the most populous city in the country, is a tourist attraction. Acropolis, which means the high city, is found in many parts of Greece, but the most important and the most famous tourist point of the region is the Acropolis of Athens. Acropolis Museum, Athens Flea Market, Olympian, Athens National Archaeological Museum, Plaka and Anafiotika districts, Panathenaic Stadium, Byzantine Museum, Cycladic Art Museum are the most important centers in this region.
Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki was founded by King Kassandros of Macedonia in 315 BC. It is one of the oldest cities in history, named after Thessaloniki, the daughter of King Philip of Macedonia. Thessaloniki is Greece's second-largest city and is located in the northern part of the country, in Central Macedonia. Thessaloniki is a popular visit point with its lively seaside street, squares, museums, and parks. Located on the shores of Thermaikos Bay, the city consists of two parts, old and new. The majority of the sights and the famous shrines of Thessaloniki are located in the old city. The White Tower on the shores of the Aegean Sea, next to the bay, is the symbol of the city today. Surrounded by lush parks and gardens, the tower is the ideal place to start exploring the city. From here, you can walk along the waterfront street and relax in one of the restaurants and cafes when you are tired.
Greek Islands
A considerable part of Greece's land is made up of islands of various sizes. As there are hundreds of islands, you may spend months in Greece and still not see many islands. When the number of islands is abundant, the variety also increases. Some islands are famous for its beaches, others for its natural beauty and archaeological ruins, and others for its crazy nightlife. Around 600 islands and islets, only 600 are open to settlements and day trips. The most popular islands of Greece are Lesbos, Chios, Kos, Santorini, Mykonos, Rhodes and Paros.
Where to Stay in Greece?
Greece offers accommodation alternatives for all budgets and tastes. If you prefer a serene holiday, you can stay in boutique hotels consisting of white houses. If you are looking for luxury 5-star hotels are ideal for you. If you are fond of history, you can stay in pensions that are built from historical buildings.
What to Eat Greece?
Greek cuisine, consisting of traditional Mediterranean products, combines exquisite flavors. Olives, olive oil, seafood, appetizers, and fresh herbs are always on the tables in Greece. Greek cuisine has many things in common with Turkish, Balkan, Italian and Lebanese cuisines. There are many common tastes shared by Turks and Greeks who have lived together for centuries: Tzatziki, Kadaifi, Dolmades, Baklavas, Moussaka, Loukoumades, Midia, and Halva.
Greek cuisine is a synthesis of Balkan and Mediterranean cuisine. Vegetables are the most important ingredients of this cuisine due to the climate and geographical location. Therefore, vegetable dishes with olive oil are among the most frequently cooked dishes. However, fish and other seafood are the most common tastes of Greek people. There is always fresh fish and the fish is prepared with years of skill. Bread is among the most consumed foods in meals. Fava on Santorini, dacos salad on Crete and mestelo on Chios are among the Greek tastes you should try.
Shopping in Greece: Best Souvenirs to Buy
On the way back from your trip, you can rejoice your loved ones with gifts unique to Greece. If you want to buy objects, you can prefer ceramic products and goddess statues which you can find especially handmade on the islands. For those who are fond of the palate, olive oil, Kavala's famous Kavala cookies, all the gummy products of Chios and olives, cheese are among the ones you can buy.
Nightlife in Greece
Nightlife and entertainment are vibrant in almost every corner of Greece. Sirtaki, which is a country-specific entertainment, is possible in many places. You can also listen to a variety of music in the bars. Hotels in Athens, in particular, offer a variety of entertainment alternatives for tourists; DJ performances and live Greek music. You can also experience Greek classics at the taverns. In the Greek islands, quiet bars on the streets and clubs on the beaches host entertainment enthusiasts.
Things to Know Before Visiting Greece
- Official working hours in Greece are from 07.00 to 14.00. The time period between 14.00-17.00 is the siesta time for the Greeks. However, after 17.00 every place does not open. Therefore, we recommend that you do your official work or shopping until 14.00.
- On Sundays, usually, all places are closed.
- If you are going to visit the Greek Islands, you should get your ferry tickets in advance in order to avoid any problems.
- Many restaurants in Greece do not accept credit cards. So don't forget to take cash and ATM cards with you.
- There is usually no lifeguard on the beaches. If you don't know how to swim well, you should be careful.
- The popularity of English speaking is quite high in touristic areas as in the whole country. If you don't speak Greek, you can easily communicate with English.
- Hospitality is very high in Greece.
- Check visa requirements at your embassy. You can learn the details of the Greece visa application process from the "Greece Visa Guide" article.
- If you like to visit the museum, you are lucky. There are more archaeological museums in Greece than any other country in the world.
Holidays in Greece
- 6 January – Epiphany
- 25 March – Independence Day
- 28 October – Ohi Day
Festivals in Greece
- Athens-Epidaurus Festival
- Thessaloniki International Film Festival
- Kalamata International Dance Festival
- Rockwave Festival
- Kalymnos Climbing Festival
- Athens Open Air Film Festival
- Sani Gourmet Festival
FAQ about Greece
Is the Macedonian Region in Greece the same as Macedonia, known as a country?
The Macedonian region, which is located in the north of Greece and Macedonia, known as the country, are separate places. The country, Macedonia, was named Northern Macedonia in 2019 and this complexity was solved.
What does the Greek Flag mean?
The 5 blue horizontal lines on the national flag symbolize the purity of Greek independence, while the 4 white lines represent the sky and the sea. The cross in the upper left corner represents Christianity.
How many regions are there in Greece?
There are 13 regions in Greece. These regions are Atika, Central and Western Greece, Central and Western Macedonia, Crete, Western Thrace, and Macedonia, Central Greece, Epirus, Ionian Islands, North Aegean Islands, Peloponnese Peninsula, South Aegean, Thessaly.
What is the official name of Greece?
The official name of Greece is the Hellenic Republic (Helliniki Dimokratia).
All Country Guides
Bosnia and Herzegovina Travel Guide
Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus Travel Guide